项目中有一个生日短信提醒功能,需要每年提醒。选农历, 每年提醒, 第二年的公历是不一样的,所以每一年的都需要自己计算。
设计的要求 ,他们说因为年纪大的人是只记得农历的。。。
网上资料不少,公历转农历现成的一堆。都是用微软的System.Globalization.ChineseLunisolarCalendar类写的,
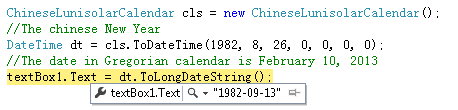
但是农历转公历的很少,也有,但都是只提到方法的调用,比如下面:
正确的应该是1982-10-12 。由于 并没有详细说到关键的闰月计算, 所以起初很困惑,以为计算不准确。
检查全年的月份,发现有因为有闰月的情况,有润月则应该从该闰月起月份自动加一, 如1982年润四月,或则闰五月为6月,后面的月加一处理。
方便理解自己做个对照图:
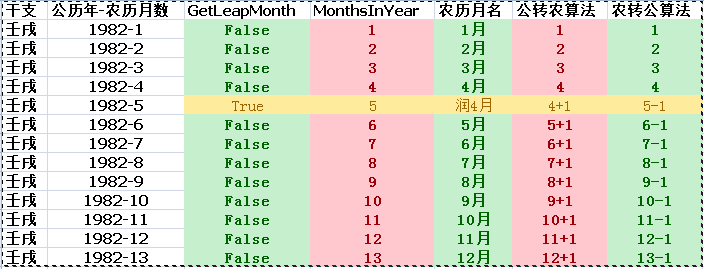
正确的方法是,要先计算当年农历生日之前的月份有没有闰月,
有了就 直接构造农历日期对象是就把农历的月+1 为9月:
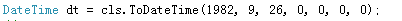
只要明白闰月这一点,其实就很简单了!
///////////
//公历转农历
///////////
DateTime date = Convert.ToDateTime(textBox1.Text); //格式:2000-1-1
ChineseLunisolarCalendar cc = new ChineseLunisolarCalendar();
if (date > cc.MaxSupportedDateTime || date < cc.MinSupportedDateTime)
MessageBox.Show("参数日期时间不在支持的范围内,支持范围:"+cc.MinSupportedDateTime.ToShortDateString()+"到"+cc.MaxSupportedDateTime.ToShortDateString());
int year = cc.GetYear(date);
int month = cc.GetMonth(date);
int dayOfMonth = cc.GetDayOfMonth(date);
int leapMonth = cc.GetLeapMonth(year);
bool isLeapMonth = cc.IsLeapMonth(year, month);
bool isLeapYear = cc.IsLeapYear(year);
if (isLeapMonth || isLeapYear && month >= leapMonth)
month -= 1;
textBox2.Text = string.Concat(year, "-", month, "-", dayOfMonth);
///////////
//农历转公历
///////////
ChineseLunisolarCalendar cc = new ChineseLunisolarCalendar();
DateTime date = Convert.ToDateTime(textBox2.Text); //格式:2000-1-1
int MonthsInYear = cc.GetMonthsInYear(date.Year);
int LeapMonth = cc.GetLeapMonth(date.Year, 1);
bool isLeapMonth = cc.IsLeapMonth(date.Year, date.Month);
bool isLeapYear = cc.IsLeapYear(date.Year);
if (isLeapMonth)
date = cc.ToDateTime(date.Year, date.Month - 1, date.Day, 0, 0, 0, 0);
else if(date.Month > LeapMonth)
date = cc.ToDateTime(date.Year, date.Month + 1, date.Day, 0, 0, 0, 0);
else
date = cc.ToDateTime(date.Year, date.Month, date.Day, 0, 0, 0, 0);
textBox1.Text = date.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd");
这是一个WinForm做的的实例Demo: WindowsFormsApplication1